|



|
Az itt látott étrend-kiegészítő megkapta az Érték és Minőség Nagydíjat.
Ezzel együtt már 23 termékünk érdemelte ki ezt a megtisztelő védjegyet, amely garancia
a minőségre valamint arra, hogy a lehető legjobb étrend-kiegészítőt használja egészsége
megőrzése érdekében.
|
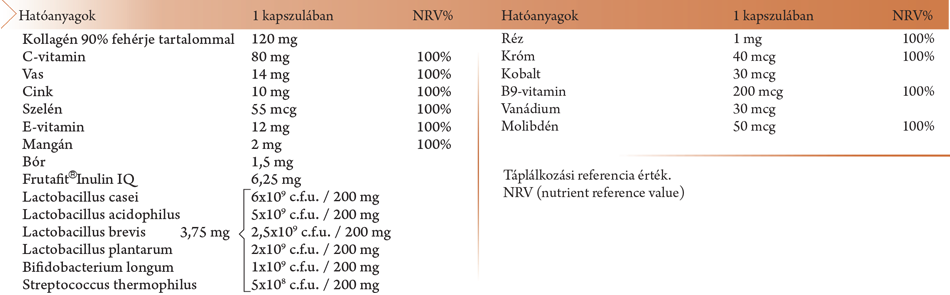
A kollagén egy természetes fehérje, mely az emberi szervezetben a fehérjetömeg 30%-át teszi ki. Elsősorban kötő- és támasztószövetekben található meg, de ez az egyik fontos építőanyaga a csontoknak, a porcoknak, az inaknak, a szalagoknak és a bőrnek is. A bőrfehérjék átlagos tömegének a 70%-a kollagén.
Ezt a fehérjét a szerveztünk képes előállítani az aminosavakból, azonban a kor előrehaladtával termelődése fokozatosan csökken.
A természetes kollagén források az állati eredetű élelmiszerek, főleg a szárnyasokban és a halakban van sok, de a gombákban is megtalálható ez az anyag. Fontos az is, hogy többféle zöldséget, magvakat és hüvelyeseket is fogyasszunk, mert a növényi fehérjék is részt vesznek a kollagén felépítésében.
Érdekesség
Már az ókori Kínában gyógyították az ízületi kopás okozta fájdalmakat marhacsontokból főtt erőlevessel. A marhacsont (elsősorban a porcos rész) alapanyaga a kollagén, ami forró vízben zselatinná alakul át.
Orvosi tanulmányok bizonyítják, hogy az inak szakítószilárdságát a kollagén-rostok mennyisége határozza meg.
A C-vitamin talán a legismertebb vitamin. A vízben oldódó vitaminok csoportjába sorolható cukorszármazék. A legtöbb állat szintetizálni tudja a saját vitaminszükségletét, ezzel szemben az embernek az étrendi forrásokra kell szorítkoznia. A C-vitamin csak igen kis mennyiségben fordul elő az állati eredetű tápanyagokban, a zöld növények, gyümölcsök fedezik a szükséglet döntő részét. Egyes növények különösen nagy mennyiséget tartalmaznak, például a csipkebogyó és egyes paprikafajok száraz súlyának 1-2 %-a C-vitamin. Tiszta állapotban mellékveséből Szent-Györgyi Albert izolálta elsőként 1928-ban, később 1931-ben citromléből és paradicsompaprikából. Ez volt az a felfedezés, melyet 1937-ben orvosi Nobel díjjal jutalmaztak.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
A citrusfélék gyümölcsei, a bogyós termések, a zöld és leveles főzelékfélék, a paradicsom, a paprika.
|
|
Miért fontos a C-vitamin?
|
|
A C-vitamin hozzájárul a normál energiatermelő anyagcsere-folyamatokhoz, a normál pszichológiai funkció fenntartásához, az idegrendszer és az immunrendszer normál működéséhez. A normál kollagénképződéshez is hozzájárul a C-vitamin, ezen keresztül a bőr, az erek, a porcok, a csontozat, a fogak és a fogíny normál állapotának fenntartásához. Segít a fáradtság és kifáradás csökkentésében, hozzájárul az E-vitamin redukált formájának regenerálásához, illetve fokozza a vas felszívódását. Hozzájárul a sejtek oxidatív stresszel szembeni védelméhez, illetve az immunrendszer normál működéséhez intenzív testmozgás alatt vagy azt követően.
A természetben elemi állapotban nem található meg, de különböző vegyületei formájában a földkéreg 4,8%-át adja. Az emberi testben mikroelemként van jelen, egy átlagos felnőtt szervezete 2,5-5 gramm vasat tartalmaz. Legnagyobb részét a hemoglobinhoz kötve, másik része pedig a különböző szállítófehérjékhez kötődik.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Korpa, aszalt sárgabarack, spenót, máj, egyéb belsőségek és a húsok.
Hozzájárul a normál vörösvérsejt- és hemoglobin-képződéshez, a normál szellemi működés fenntartásához, az immunrendszer normál működéséhez és a fáradság és a kifáradás csökkentéséhez. Szerepet játszik a sejtosztódásban. Részt vesz a normál oxigén szállításban és a normál energiatermelő anyagcsere-folyamatokban.
Ez az ásványi anyag szobahőmérsékleten kékes színű, rideg, fémes elem. Neve a német Zink névből ered, magyarul horganynak is nevezik.
Ötvözetek formájában a cinket már az ókorban is ismerték, de magát az anyagot csak 1300 körül állították elő. Emberi szervezetben betöltött szerepére sokáig nem gondolt senki.
A szervezetben 2-3 grammnyi cink van, főleg a haj, a szem és a férfi nemi szervek tartalmazzák, de megtalálható még a májban, a vesékben, az izmokban és a bőrben is.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Tojás, hüvelyesek, máj, tenger gyümölcsei, rák, tökmag, gabonacsíra, olajos magvak.
A cink részt vesz a normál szénhidrát-anyagcserében, a makrotápanyagok, a zsírsavak és az A-vitamin normál anyagcseréjében, valamint a normál sav-bázis egyensúly fenntartásában. Hozzájárul a normál csontozat, a normál látás, a haj, a köröm és a bőr normál állapotának fenntartásához. Továbbá hozzájárul az immunrendszer normál működéséhez, a sejtek oxidatív stresszel szembeni védelméhez, a normál szellemi működés fenntartásához, a normál DNS-szintézishez és a vér normál tesztoszteron szintjének fenntartásához. Szerepet játszik a sejtosztódásban, a normál fehérjeszintézisben és a normál termékenység és szaporodás fenntartásában.
Nevét Szelénéről kapta, a görög mitológia Hold istennőjéről. Az 1800-as évek végére bizonyították be, hogy nélkülözhetetlen nyomelem a szervezet számára, mivel egy bizonyos glutation-peroxidáz nevű enzimet tartalmaz, mely megvédi a szervezetet a testünkbe került mérgekkel szemben. A szelén csupán 10-15 mg mennyiségben található meg az emberi szervezetben.
A szelén legfőbb természetes forrásai
Paradió, tonhal, napraforgómag, rizs, vörös húsok szárnyasok, teljes kiőrlésű lisztből készült pékáruk, kesudió.
Az E-vitaminnal kölcsönösen fokozzák egymás jótékony hatását, így hozzájárulnak a sejtek oxidatív stresszel szembeni védelméhez. Ezenfelül a szelén hozzájárul a köröm, illetve a haj normál állapotának fenntartásához, valamint a normál pajzsmirigy és immunrendszer működéséhez.
Zsíroldékony vegyület, amely a májban, a zsírszövetekben, a szívben, az izmokban, a vérben, a mellékvesékben és az agyalapi mirigyben raktározódik. Az E-vitamint a XX. század 20-30-as évei közt, a növényi olajok tanulmányozására irányuló kísérletek folytatása közben fedezték fel, majd izolálták, azonban csak a hetvenes években jöttek rá, hogy az ember számára létfontosságú anyagot fedeztek fel. Ellentétben a többi zsíroldékony vitaminnal, az E-vitamin, akárcsak a B-vitaminok vagy a C-vitamin, aránylag rövid ideig marad a szervezetben.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Búzacsíra, szójabab, növényi olajok, brokkoli, kelbimbó, spenót, teljes gabonamagvak, tojás.
|
|
Miért fontos az E-vitamin?
|
|
Hozzájárul a sejtek oxidatív stresszel szembeni védelméhez.
Ezüstszürke, rideg, az átmenetifémek közé tartozó nyomelem. A természetben előforduló mangánvegyületeket az őskorban festékként használták. A kitermelt mangán 90%-át az acélgyártásban hasznosítják, így gazdasági szempontból is fontos elem. A mangán számos enzim alkotórésze, így a fotoszintézisben is központi helyet foglal el, ezáltal biológiai szempontból is nagy jelentőségű. Az emberi test 10-20 mg mangánt tartalmaz, ami többek között a csontokban is raktározódik. Az emberi szervezet számos élettani folyamat fiziológiás működéséhez elengedhetetlen, több fontos enzim megfelelő működéséhez is szükséges. A mangán hozzájárul a normál csontozat fenntartásához és a normál kötőszövetképződéshez.
1808-ban fedezte fel három kémikus. Meglehetősen ritka mikroelem. Legismertebb vegyületei a bórsav és a bórax.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Leveles zöldségek, olajos magvak, gyümölcsök, gabonamagvak, szójabab, lazac, szardínia, sajt.
A réz az egyik leggyakrabban és legrégebb óta használt fém, melynek jelenléte a szervezetünkben számos folyamat lezajlásához szükséges.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Paradicsomos szardínia, napraforgómag, rák, homár, földimogyoró, osztriga, aszalt szilva.
A réz a szervezetben hozzájárul a normál energiatermelő anyagcsere-folyamatokhoz, az idegrendszer normál működéséhez, a haj és a bőr normál pigmentációjához, az immunrendszer normál működéséhez.
Legnagyobb mennyiségben a Föld belsejében található, de a földkéregben és a felszíni vizekben is jelen van. Legtöbbször ércekben található meg, mivel elemi állapotban nem fordul elő. Az emberi szervezetben mindössze 1-2 milligrammnyi kobalt található, amely a B12-vitaminnal fontos szerepet játszik a szervezetünk normál működésében.
A B9-vitamin vagy más néven folsav vízben oldódó vegyület, amely valójában nem egyetlen, hanem több hasonló felépítésű és hatású pteridin-származék. A folsav felfedezéséhez dr. Lucy Wills anémiás embereken élesztővel végzett kísérletei vezettek az 1930-as években.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
A leveles zöldségek (kelbimbó, brokkoli, saláta, paraj), fekete szemű bab, máj, élesztő, földimogyoró, dió.
1830-körül fedezték fel. A nevét a norvég Vanadis istenről kapta, aki a szépség és a termékenység istennője.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Gomba, gabonafélék, olajos magvak, borok, gyümölcslevek, petrezselyem, rákok és egyéb tengeri élőlények.
A szervezetünkben nagyon kis mennyiségben van jelen, ennek ellenére nélkülözhetetlen az egészséges emberi szervezetből. A molibdén hozzájárul a kéntartalmú aminosavak normál anyagcseréjéhez.
Legfőbb természetes forrásai
Bab és hüvelyesek, spenót, barna rizs, belsőségek, lencse, tej, olajos magvak, gabonafélék.


Ez a One Year Product termék hatféle élőflórát tartalmaz emelt csíraszámban, továbbá a hatékonyságot növelő Inulint.
Inulin és élőflóra
Az élőflórát olyan jótékony, élő mikroorganizmusok alkotják, melyek a tápcsatornában a savas közeget is túlélve segítik a bélflóra egészséges egyensúlyának fenntartását. Termékeink magas csíraszámban tartalmaznak több élőflórát és a szaporodásukat elősegítő Inulint. A Probiotikum más néven élőflóra kifejezés görög eredetű, jelentése: az életért. A mai értelemben R. B. Parker alkalmazta először a probiotikum kifejezést 1974-ben, mint azokat az organizmusokat és anyagokat, amelyek a bélrendszer mikroba-egyensúlyáért felelősek. A probiotikumok jellemzői, hogy emberi eredetűek, nem kórokozók, ellenállnak a gyomorsav, az epe, valamint a nyál, a hasnyálmirigy és a bélnedvek emésztő enzimei hatásának. Az élelmiszerek szavatossági idejének tartalma alatt és a technológiai folyamatok során megőrzik ellenállóképességüket. Ezen kívül a probiotikumok képesek a nyálkahártyák sejtjeihez tapadni, a potenciális kórokozók ellen antimikrobás hatást fejtenek ki, csökkentik a kórokozó mikrobák megtapadását a nyálkahártya felszínén. A probiotikumok legnagyobb részben tejsavbaktériumok és bifidobaktériumok. A legismertebb probiotikus tejsavbaktérium-törzsek többsége a Lactobacillus, kisebb része a Streptococcus nemzetséghez tartozik. Prebiotikumoknak nevezzük azokat a természetes tápanyagokat, amelyek jellemzően a probiotikumok kizárólagos tápanyagai, ezért elősegítik azok elszaporodását és túlsúlyba kerülését. A szájüregben, illetve a gyomor-bélcsatornában az emésztőenzimek nem bontják le a prebiotikumokat, így emésztetlenül juthatnak a vastagbélbe. A prebiotikumok diétás rostok, de vízben oldhatók, ezért a diétás rostok közül is a legkiválóbbak. Élelmi rost funkciójuk mellett igazi hasznosságuk abban rejlik, hogy a probiotikumok kizárólagos táplálékai. Mivel a vastagbélben már kevés az emészthető táplálék, vagyis ott relatív táplálékhiány van, az elfogyasztott prebiotikumok lehetőséget kínálnak a humánbarát bélbaktériumok elszaporodására. Természetes állapotukban sok élelmiszerben előfordulnak, pl: csicsóka, cikóriagyökér, vöröshagyma, fokhagyma, póréhagyma, articsóka, teljes értékű gabonamagvak, búza, banán, len, spenót, káposztafélék, mangold, mustárfélék, bogyós gyümölcsök, hüvelyesek, tej és az érett sajtok többsége. A prebiotikumok egyik fajtája az Inulinok, tulajdonképpen egy diétás rost, mely emésztetlenül jut el a vastagbélbe, fokozzák a probiotikumok szaporodását, túlsúlyba kerülésüket. Szerepük: emésztés, bélflóra egyensúlya
A szervezetünk legnagyobb felszínnel rendelkező, mintegy 7-9 méter hosszúságú bélrendszerünkön keresztül áll kapcsolatban a külvilággal. Így potenciális támadási helyként szolgál a kórokozók és a toxikus anyagok számára. A bélben normális körülmények között mintegy 200-400 baktériumtörzs található. A magzati életben a jótékony baktériumok 95-98%-ban vannak túlsúlyban. Az egészséges bélflóra védelmet biztosít számos kórokozóval szemben, biztosítja a bélnyálkahártya épségét és segíti a szervezet számára szükséges tápanyagok felszívódását. Számos, a szervezet számára nélkülözhetetlen vitamint termelnek. Ha az emésztőrendszer védelmi mechanizmusai gyengülnek, az többek között felszívódási folyamatok zavarát okozhatja. A probiotikumok ahhoz, hogy képesek legyenek környezetükre hatást gyakorolni, a nagyszámú jelenlét alapfeltétel, mely a bélfolyadékban grammonként legalább 108 c.f.u. organizmust jelent. | Mit jelent a c.f.u. kifejezés? c.f.u.: kolóniaképző egység milliliterenként, az életképes mikroorganizmusok száma (csíraszám). A készítményekben általában ilyen egységben adják meg a baktériumok mennyiségét. Az Inulint azonban mg-ban határozzák meg. Megfelelő dózisnak a minimum 109 c.f.u. az elfogadott. | |
| Milyen a hatékony élőflórás készítmény? - | A probiotikumok szaporodását a prebiotikumok elősegítik, ezért tartalmazzon a készítmény Inulint vagy frukto-oligoszacharidákat. | | - | Ellenállnak a gyomorsav, az epe, illetve az emésztőenzimek hatásainak, így élve el tudnak jutni a hasznos baktériumok a vastagbélbe, ahol képesek elszaporodni és megtapadni. Alapvető kritérium, hogy a baktériumok megtartsák életképességüket a gyomor-bélrendszerben történő áthaladásuk során. | | - | A jó élőflórás készítmények minimum 5-6 törzset tartalmaznak, hiszen a bélbaktériumok sokrétű multikultúráját kívánjuk pótolni. | | - | Szavatossági idő alatt és a technológiai folyamatok során megőrzik ellenálló képességüket. | | - | Megfelelő mennyiségű csíraszámot tartalmaz, szakemberek által javasolt
minimum 108 vagy 109 telepképző egység. |
| |
|